Plastic injection molding vs 3D printing
Choosing the right technology to manufacture your next plastic part
With 3D printing rising in popularity in recent years, our team at Nelson Miller Group is often asked to compare plastic injection molding vs 3D printing. When it comes to manufacturing plastic parts, both are very popular methods and are often thought of as competing technologies. But there are enough differences that one typically stands out as a much more suitable method, depending on the customer’s use case. Let’s take a closer look to better understand injection molding and 3d printing in manufacturing plastics.
What’s plastic injection molding and how is it used?
Plastic injection molding involves injecting molten resin into a plastic injection mold to create a part. The process uses a plastic injection molding machine to melt plastic granules and force them into a pre-designed mold under high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens to release the part.
Plastic injection molding is commonly used for mass production of high-volume parts, from tiny screws to large home appliances. Some of the benefits of plastic injection molding are its efficiency in large-scale production and ability to create durable, high-quality parts, making it ideally suited for a number of applications:
- In the automotive industry, where precision and consistency are critical, injection molding allows manufacturers to produce complex parts like bumpers, dashboards, and interior trims with high accuracy and uniformity. The cost-effectiveness of the process for large volumes also makes it a perfect fit for the automotive sector.
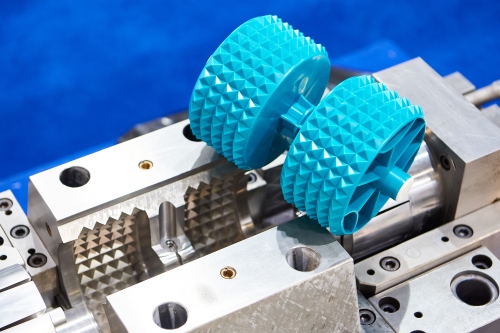 In the realm of consumer goods, the flexibility material selection and finishing options makes it possible to produce a wide array of injection molded products—from kitchen utensils to outdoor furniture—with varying degrees of complexity.
In the realm of consumer goods, the flexibility material selection and finishing options makes it possible to produce a wide array of injection molded products—from kitchen utensils to outdoor furniture—with varying degrees of complexity. - Electronic housings require the precise tolerances and durable materials available with injection molding, ensuring components fit together seamlessly while maintaining safety and performance standards.
- The toy industry, which relies on colorful, intricate designs, benefits from the versatility of injection molding in creating both detailed and sturdy products.
- In medical devices, where safety and reliability are paramount, injection molding's high precision and ability to use medical-grade plastics make it a trusted manufacturing method for items like syringes, IV components, and various surgical tools.
3D printing and its ideal applications
3D printing is also called additive manufacturing because it builds up parts layer-by-layer from digital models in an additive process. A design is created using computer-aided design (CAD), then sent to a 3D printer, which constructs the part by adding material in successive layers. 3D printing in manufacturing has grown in popularity due to its ability to create complex shapes and custom parts quickly. It’s become a preferred method for prototyping, small-batch production, custom parts, aerospace components, and medical devices, primarily due to its flexibility and reduced setup costs.
When it comes to prototyping, the speed and flexibility of 3D printing allow designers and engineers to quickly iterate on designs without the need for expensive molds. This capability makes it easier to test new ideas and refine products before committing to large-scale production.
 For small-batch production, especially in industries where customization is key, one of the benefits of 3D printing is the ability to produce parts on demand without the need for extensive tooling. This is particularly useful in the aerospace industry, where lightweight, complex parts are required, and traditional manufacturing methods might be too slow or costly. The ability to create intricate geometries and lightweight structures makes 3D printing an attractive choice for aerospace applications.
For small-batch production, especially in industries where customization is key, one of the benefits of 3D printing is the ability to produce parts on demand without the need for extensive tooling. This is particularly useful in the aerospace industry, where lightweight, complex parts are required, and traditional manufacturing methods might be too slow or costly. The ability to create intricate geometries and lightweight structures makes 3D printing an attractive choice for aerospace applications.
In the medical field, 3D printing in manufacturing has revolutionized the production of custom prosthetics, dental devices, and surgical instruments. The technology's adaptability allows for bespoke designs tailored to individual patients, providing a level of personalization that is difficult to achieve with traditional methods. Additionally, the range of materials available for 3D printing—including biocompatible plastics and metals—ensures that the parts produced meet stringent medical standards.
Comparing plastic injection molding vs 3D printing
Here's a detailed table comparing plastic injection molding vs 3D printing across six key factors:
| Factor | Plastic injection molding | 3D printing |
| Cost considerations | High initial setup costs due to mold creation. Cost-effective for large production runs. | Lower initial costs, especially for prototyping and small-batch production. Cost per part is higher for larger runs. |
| Materials options | Extensive range of plastics and additives. Suitable for high-strength and heat-resistant applications. | Wide variety of materials. Flexible material options, but not as durable as injection molding materials. |
| Design complexity and flexibility | Limited by mold design but can achieve intricate details with proper tooling. | Highly flexible, allowing for complex geometries and intricate designs that might be impossible with traditional molds. |
| Speed of production | Extremely fast for high-volume production. Ideal for scalability and mass production. | Slower production time for large batches. Ideal for quick prototyping and low-volume manufacturing. |
| Surface finishing and post-processing | Generally requires additional finishing for complex parts. Can achieve smooth surfaces with proper polishing. | Minimal post-processing but may require support removal and surface finishing. Finishes are generally not as smooth as injection molding. |
| Quality | High precision with tight tolerances. Suitable for critical applications where accuracy is crucial. | Adequate precision, but generally not as accurate as injection molding. Ideal for prototypes and custom parts with less stringent requirements. |
Making the choice between injection molding and 3D printing
 Both plastic injection molding and 3D printing have their benefits and limitations. The right choice depends on your specific project requirements, including cost, production volume, design complexity, and quality needs. Understanding the specific demands of your project is key to making the right choice. Ultimately, for medium- to long-run production injection molding is the cost-effective choice, offering high precision and extensive material options.
Both plastic injection molding and 3D printing have their benefits and limitations. The right choice depends on your specific project requirements, including cost, production volume, design complexity, and quality needs. Understanding the specific demands of your project is key to making the right choice. Ultimately, for medium- to long-run production injection molding is the cost-effective choice, offering high precision and extensive material options.
At Nelson Miller Group, we understand that making this decision can be challenging. Our experienced team can offer tailored advice and solutions to help you select the manufacturing method that best suits your needs. With our expertise, you'll gain access to state-of-the-art technology, extensive material options, and a partner committed to your success. Contact us today to find out how we can support your next project.

About NMG
NMG has more than 85 years of experience partnering with organizations to bring their industrial, IoT, lighting, medical, telecommunications, consumer, and aerospace products to life. We solve your most complex challenges in engineering design, manufacturing, and supply chain management.
Follow NMG
Could your company use results like this?
We want to learn about your organization and understand your unique challenges.