Popular specialty finishes in plastic injection molding
Plastic injection molding has become an indispensable manufacturing process, known for its efficiency and ability to produce complex and high-quality parts. One of the key advantages of this process is the variety of specialty finishes that can be applied to molded parts. These finishes are crucial not only for enhancing aesthetic appeal, but also for improving functionality and performance.
The VDI 3400 and SPI Finish are the two most widely used surface finishes for plastic injection molds. They make up the majority of finish options available. This blog explores these two finish standards as well as some of the most popular specialty finishes requested by manufacturers. We will delve into how various finishes impact product design and manufacturing processes, and highlight potential pitfalls associated with each.



SPI (Society of the Plastics Industry) finishing standards
The SPI, now known as the Plastics Industry Association, has established a comprehensive set of finishing standards for plastic injection molded parts. These standards categorize finishes into four distinct grades: Diamond Buff (A-1 to A-3), Paper (B-1 to B-3), Grit (C-1 to C-3), and Dry Blast (D-1 to D-3). Each category specifies the surface roughness and polishing methods required to achieve the desired finish. For instance, A-1 indicates the highest quality, mirror-like finish, while D-3 denotes a rough, non-reflective surface. Adhering to SPI standards ensures consistency, reliability, and quality across different manufacturers and applications, making it easier to meet industry-specific requirements.
VDI surface finish standards
The VDI (Association of German Engineers) surface finish standards provide a detailed framework for specifying surface textures on molded parts. These standards are widely recognized in Europe and are increasingly adopted globally. VDI standards use a scale from VDI 0 (mirror finish) to VDI 45 (rough texture), with each grade defined by a specific range of roughness values (Ra). This precise classification allows for accurate replication of surface textures, ensuring consistency across production batches. VDI finishes are particularly beneficial in industries requiring high precision and uniformity, such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
ProtoMold (PM)
ProtoMold, or PM, refers to a specialized service provided by some manufacturers to produce rapid prototypes and short-run production parts. This process utilizes high-speed CNC machining and advanced molding techniques to deliver high-quality plastic parts in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. PM focuses on achieving functional prototypes with excellent surface quality, enabling quick iterations and design validation. This approach is particularly valuable in industries with fast-paced development cycles, such as electronics, automotive, and medical devices, where time-to-market is a critical factor.
Most popular injection molding finishing techniques
Polishing
Polishing is a critical post-molding process for achieving smooth, glossy surfaces on plastic parts. It involves the careful removal of material through mechanical or chemical processes to achieve the desired surface finish. There are several grades of polishing, ranging from high-gloss mirror finishes to matte or semi-gloss finishes.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Polished finishes are particularly important in applications requiring optical clarity or aesthetic appeal, such as automotive interiors, consumer electronics, and medical devices. The level of polish directly influences the visual and tactile quality of the product, impacting user perception and functionality. The precision of polishing enhances a product’s ability to meet stringent industry standards.
Potential pitfalls
Achieving a high-gloss finish can be time-consuming and costly. Additionally, highly polished surfaces are more susceptible to scratches and may require additional protective coatings.
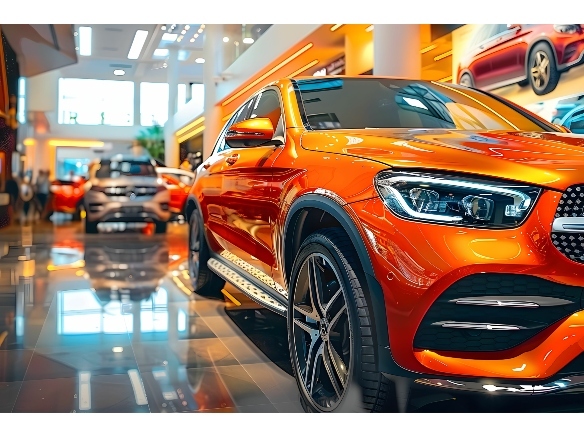

Texturing

Texturing adds controlled surface patterns to plastic parts, which can enhance both their functional and aesthetic properties. Common methods include chemical etching, laser texturing, and mechanical engraving.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Texturing can improve grip, reduce glare, hide imperfections, and create attractive designs. It’s widely used in automotive interiors, consumer goods, and electronics to provide a premium look and feel. Moreover, texturing can influence the part's performance by affecting its friction and wear resistance.
Potential pitfalls
Texturing can complicate the molding process, as it may require precise control over mold temperature and material flow to ensure uniform patterns. Additionally, intricate textures may increase mold maintenance and cleaning requirements.
Silkscreen printing
Silkscreen printing is a popular technique for applying detailed graphics, text, and symbols onto plastic parts. It involves using a mesh screen to transfer ink onto the surface of the molded part through a stencil.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Silkscreen printing offers high versatility and is ideal for adding logos, labels, and intricate designs to products. It’s widely used in consumer electronics, automotive components, and medical devices. This method allows for vibrant, multi-color prints with excellent adhesion and durability.
Potential pitfalls
The primary challenge with silkscreen printing is ensuring consistent ink application, especially on complex or curved surfaces. Additionally, the process can be time-consuming and less cost-effective for small production runs due to the setup required for each color layer.
Pad printing
Pad printing, also known as tampography, is used to transfer images onto irregular or curved surfaces. It involves using a silicone pad to pick up ink from an etched plate and transferring it onto the part.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Pad printing is highly effective for decorating parts with intricate details, making it suitable for applications in medical devices, automotive interiors, and consumer goods. It provides excellent print quality and precision, even on uneven surfaces.
Potential pitfalls
Pad printing can be limited by the size and depth of the design, as very fine details may not transfer accurately. Additionally, the process can be relatively slow and labor-intensive, making it less suitable for high-volume production.
Laser etching
Laser etching uses focused laser beams to create permanent markings on the surface of plastic parts. This process can engrave detailed patterns, text, and logos with high precision.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Laser etching is ideal for applications requiring high-resolution, durable markings, such as branding, serial numbers, and barcodes in the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries. It offers flexibility, as it can be easily adjusted for different designs without the need for physical tools or dies.
Potential pitfalls
The initial setup cost for laser etching equipment can be high. Additionally, the process may affect the mechanical properties of the plastic if not properly controlled, potentially leading to surface degradation or changes in material characteristics.

Electroplating
Electroplating involves coating plastic parts with a thin layer of metal to enhance their appearance and provides additional properties such as conductivity, corrosion resistance, and increased strength.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Electroplating is widely used in automotive trim, consumer electronics, and decorative items. It can significantly enhance the aesthetic appeal and durability of plastic parts, making them more resistant to wear and environmental factors.
Potential pitfalls
Electroplating requires careful surface preparation to ensure proper adhesion of the metal layer. Any imperfections in the plastic surface can lead to defects in the plating. Additionally, the process involves hazardous chemicals, necessitating strict environmental and safety regulations.
Hot stamping
Hot stamping transfers foil or pre-dried ink onto plastic parts using heat and pressure. This process is often used to apply metallic finishes, logos, and decorative designs.
Impact on product design and manufacturing
Hot stamping provides a high-quality, durable finish that can simulate the look of metal, making it popular in automotive interiors, cosmetic packaging, and consumer electronics. It allows for precise application of decorative elements with excellent adhesion and resistance to wear.
Potential pitfalls
Hot stamping can be limited by the complexity of the design and the shape of the part. It may not be suitable for intricate or highly detailed patterns. Additionally, the process can be more expensive than other printing methods due to the need for custom dies and foils.
Specialty finishes play a critical role in injection molding
The diverse range of specialty finishes in plastic injection molding underscores the process's adaptability and precision. From enhancing visual appeal to imparting functional properties, these finishes are integral to meeting the stringent demands of modern manufacturing. By understanding the impact of these finishes on product design and manufacturing processes, design engineers can make informed decisions to optimize product performance and manufacturing efficiency. While each finish presents its own set of potential pitfalls, careful planning and execution can mitigate these issues, ensuring high-quality results. As technology advances, the ability to apply and perfect these specialty finishes will continue to be a vital aspect of modern manufacturing, driving innovation and meeting the demands of diverse industries.

About NMG
NMG has more than 85 years of experience partnering with organizations to bring their industrial, IoT, lighting, medical, telecommunications, consumer, and aerospace products to life. We solve your most complex challenges in engineering design, manufacturing, and supply chain management.
Follow NMG
Could your company use results like this?
We want to learn about your organization and understand your unique challenges.